English Learner Services
LINGUISTIC DIVERSITY OF OUR COMMUNITY OF LEARNERS
LINGUISTIC DIVERSITY OF OUR COMMUNITY OF LEARNERS
Multilingual learners come to school with a wide range of cultural and linguistic backgrounds, experiences with formal schooling, proficiency with native language and English literacy, immigrant, migrant and socioeconomic status, as well as interactions in the home, school, and community.According to the California Department of Education, multilingual learners constitute 39.5 percent of the state's public school enrollment, with 81.90 percent being Spanish speakers. 39 percent of Inglewood Unified are also multilingual learners; 98.1 percent of which are Spanish speakers. The figures below illustrate the linguistic diversity of our learners.



Understanding the differences between the ELAS terms is critical for determining which population of students is being discussed, although the primary focus of this master plan is to provide educators with critical information related to the linguistic and educational needs of English Learners, as well as the legal requirements for serving these students.
The California Department of Education (CDE) defines an English Learner as a student who enrolls in a California school beginning in any grade level, kindergarten through grade twelve, has a language other than English identified on the Home Language Survey (HLS), and upon assessment, obtains a level of English proficiency that indicates programs and services are necessary.
In order to provide effective targeted instruction and support, it is important to further identify their needs according to their cultural background and linguistic areas of growth:
To Be Determined (TBD) is a temporary term used for a student in kindergarten through grade 12 for whom there is a report of a primary language other than English on the HLS and for whom the district has not completed the assessment process. The assessment process must be completed within 30 days of initial enrollment.
IDENTIFICATION OF ENGLISH LEARNERS
IDENTIFICATION OF ENGLISH LEARNERS
Determination of Student's Primary Language
The HLS is required by law and must be completed and signed by a parent or legal guardian upon initial registration of TK-12 grade students enrolling in a California public school for the first time. New students may include, but are not limited to migrant, immigrant, out of state transfers, special, private or alternative education transfers, transitional kindergarten (TK), and kindergarten students.
- Which language did your child learn when he/she first began to talk?
- Which language does your child most frequently speak at home?
- Which language do you (the parents or guardians) most frequently use when speaking with your child?
- Which language is most often spoken by adults in the home? (parents, guardians, grandparents, or any other adults)
Identification of English Learners

LANGUAGE INSTRUCTIONAL PROGRAMS & ELD SERVICES
LANGUAGE INSTRUCTIONAL PROGRAMS
More than one program may exist within a given classroom. It is extremely important that students are clearly identified by program, and that they receive the appropriate English Language Development (ELD) services. Services vary among programs, and look different in each classroom. This requires differentiation of instruction and of activities within the classroom, and careful monitoring to ensure that the guidelines for each program are followed.
- Develop English proficiency
- Provide access to core curriculum
- Promote academic achievement
- Foster cultural competence and inclusion
- Provide support for transition and integration
- Promote parental and community engagement
- Targeted instruction in English language skills
- Strategies to ensure ELs understand and engage with the core curriculum
- Regular assessments to track language and academic progress
- Training for teachers to effectively support EL students
- Inclusion of students’ cultural backgrounds in the current curriculum
- Engagement of EL families in the educational process
English Language Mainstream (ELM)
The English Language Mainstream program is an optional placement for students with “reasonable fluency”, usually in the Bridging ELD level. The program may be provided in a classroom that may also contain English Only students, Fluent English Proficient students, and some English Learners with “less than reasonable fluency”, students in the Emerging or Expanding levels, whose parents have requested this placement.Structured English Immersion (SEI)
h proficiency.
Two-Way Language Immersion (DLI)
In the DLI program, literacy development in both languages is available to all students – EO, IFEP, RFEP, as well as English Learners, usually in the Emerging or Expanding ELD levels. The aim is to create a balanced and immersive educational environment where students can achieve fluency and literacy in two languages while developing a deep understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures.
The program is open to students entering a transitional kindergarten, kindergarten or first grade level; or to any newcomer in any other grade level who has had formal schooling in Spanish in another country or via a DLI program outside the district. This program is only available at Woodworth Monroe.
One-Way Language Immersion (FLES)
Parent's Right to Decline, Choose or Request a Program
Their engagement strengthens learning support at home, enhances student motivation, and upholds their rights in the decision-making process. Under California Education Code, parents have the right to decline the standard placement, choose a different program, or request an alternative program. This legal provision reinforces their role in shaping their student’s language development, ensuring that the chosen program aligns with both educational goals and cultural identity.

Process to Choose, Decline or Request a Program
ENGLISH LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT SERVICES
Appropriate English language development services and education programs enable English Learner students to attain both English proficiency and parity of participation in the regular education program within a reasonable amount of time. These services are offered until English Learners are proficient in English and can participate meaningfully in education programs without language support.Many factors help determine which language development services are best suited for English Learners, including proficiency, grade level, educational and language background, disabilities, and whether the services are required or supplemental. Services designed to meet their diverse needs encompass a range of approaches and resources tailored to support their language acquisition and academic success.
English Language Development Instruction (Required)
Designated ELD instruction is provided during a time set aside in the regular school day, focused on the CA ELD Standards to assist English Learner students to develop critical English language skills necessary for academic content learning in English. The focus is solely on language development, addressing skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Lessons are designed around language objectives that are appropriate for the students' English language proficiency levels. Designated ELD in Inglewood Unified must be:
- Included in the school’s master schedule
- Included in the student’s daily schedule
- Provided daily, for at least 45 minutes, or a full class period
- CA ELD Standards-based
- Leveled by students’ assessed English language proficiency
Integrated ELD is incorporating English language instruction into regular content area teaching, ensuring that English Learners simultaneously develop language skills and subject matter knowledge, using the CA ELD Standards in tandem with the common core standards for ELA/Literacy and other content areas. Integrated ELD includes Specially Designed Academic Instruction in English (SDAIE) and may include primary language support. Integrated ELD in Inglewood Unified must be:
- Provided daily, in all core subjects by all teachers of ELs, including special education settings
- Designed to provide meaningful access to the core curriculum
- CA Standards-based

Primary Language Support (Supplemental)
Bilingual Dictionaries provide students with a valuable resource for understanding new vocabulary by offering translations and definitions in their native language. This support helps students comprehend instructions, texts, and assignments more easily, facilitating smoother transitions to English fluency. By enabling quick reference and clarification, bilingual dictionaries enhance students' reading and writing skills and boost their confidence in using English.
Reading Books in Spanish enable students to practice reading in their native language while gradually building their English literacy skills. Access to literature in their language helps students develop a love for reading, supports their bilingualism, and allows them to connect their learning to their cultural background, enhancing overall comprehension and engagement.
Bilingual In-class Tutors offer personalized support by providing individual or small group instruction in both English and the student's native language. This tailored assistance helps students grasp difficult concepts and bridge language gaps, fostering better understanding and retention of the core material. Bilingual tutors can also offer cultural insights and emotional support, creating a more inclusive and supportive learning environment that encourages academic success.
Core Curriculum Materials in Spanish such as textbooks and workbooks in both English and the native language, provide students with the ability to access the same content as their peers while still receiving primary language support. These materials ensure that students can follow along with lessons, complete assignments, and understand subject matter without being hindered by language barriers. This dual-language approach helps maintain academic progress while simultaneously building English proficiency, leading to better educational outcomes.
Electronic Translators provide essential primary language support to English Learners (ELs) in the classroom by enabling immediate translation of words, phrases, and sentences between the student's native language and English. These devices or applications facilitate understanding of instructions, content, and classroom interactions, thereby bridging language gaps that might otherwise hinder learning. By offering real-time translations, electronic translators help ELs grasp complex concepts, participate actively in discussions, and complete assignments more effectively. This support not only enhances comprehension but also boosts confidence, allowing ELs to engage more fully in the educational experience while they develop their English proficiency.
Together, these primary language resources play a crucial role in supporting English Learners by making educational content accessible, promoting understanding, and fostering an inclusive learning environment. By removing language barriers, we can better support students to achieve academic success while developing their English skills.
Digital Learning Tools (Supplemental)
The Inglewood Unified School District is committed to delivering more equitable learning experiences to every student by providing teachers and students with the tools they need for success. Technology-based tools are carefully selected to supplement and support better academic outcomes for all students.
Google Workspace for Education offers various tools like Google Docs and Google Slides, which have built-in translation features that provide primary language support.. These tools allow students to translate documents and presentations into their native language, aiding comprehension of assignments and classroom materials. By facilitating understanding and allowing students to work in both their native language and English, these features help students grasp complex concepts, stay on track with their coursework, and build confidence in their language skills.
Nearpod EL offers interactive lessons that integrate ELD support, making content accessible to English Learners. These lessons include visuals, audio, and interactive activities that are designed to scaffold learning and provide language support. By offering content in an engaging and comprehensible manner, Nearpod helps students to better understand subject matter, participate actively in class, and enhance their English proficiency.
ENGLISH LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY ASSESSMENTS FOR CALIFORNIA (ELPAC)
ENGLISH LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY ASSESSMENTS FOR CALIFORNIA (ELPAC)
 Federal law requires that schools administer a state test of English language proficiency (ELP) to eligible students in kindergarten through grade twelve. The English Language Proficiency Assessments for California (ELPAC) is the mandated state test for determining English language proficiency (ELP).
Federal law requires that schools administer a state test of English language proficiency (ELP) to eligible students in kindergarten through grade twelve. The English Language Proficiency Assessments for California (ELPAC) is the mandated state test for determining English language proficiency (ELP).Types of ELPAC Assessments
- A Parent Guide to Understanding the Initial English Language Proficiency Assessments for California
- Una Guía de Comprensión Para Padres de las Evaluaciones Iniciales de Dominio del Idioma Inglés para California
- A Parent Guide to Understanding the Summative English Language Proficiency Assessments for California
- Una Guía de Comprensión Para Padres de las Evaluaciones Sumativas de Dominio del Idioma Inglés para California
- A Parent Guide to Alternate English Language Proficiency Assessment for California
- Una Guía de Comprensión Para Padres Evaluaciones Alternativas de Dominio del Idioma Inglés para California


Practice & Training Tests
The practice test includes examples of all the types of test questions that may appear in the actual test at each grade or grade span and mirrors a full-length operational test. The training test is shorter compared to the practice test and includes some sample test questions for each domain.
How to Start a Practice or Training Test
Cómo iniciar una prueba de práctica o capacitación
Student Scores & Results


ELPAC Performance Levels & Descriptors

NOVICE (EL) - Students at this level have minimally developed oral and written English skills. They tend to rely on learned words and phrases to communicate meaning at a basic level. They need substantial-to-moderate linguistic support to communicate in familiar social and academic contexts; they need substantial linguistic support to communicate on less familiar tasks and topics.
LEVEL 1 - English learners at this level have minimally developed oral (listening and speaking) and written (reading and writing) English skills. They tend to rely on learned words and phrases to communicate meaning at a basic level. They need substantial-to-moderate linguistic support to communicate in familiar social and academic contexts; they need substantial linguistic support to communicate on less familiar tasks and topics. This test performance level corresponds to the “Emerging” proficiency level as described in the CA ELD Standards.
NOVICE EL - Students at this level have minimal English language proficiency. They need substantial linguistic support to enable them to access adapted grade-level content in English.
CONSIDERATIONS FOR ENGLISH LEARNERS WITH DISABILITIES
SPECIAL EDUCATION REFERRAL & ASSESSMENT FOR ENGLISH LEARNERS WITH DISABILITIES
Student Success Team (SST) Considerations- Systematic carefully planned, designated and integrated ELD instruction
- Daily designated ELD instructional time
- Emphasis on academic English language skills in all subject areas (integrated ELD)
- Explicitly teaching the principle components of literacy including phonics, phonemic awareness, reading fluency, vocabulary comprehension, and writing
- Increased opportunities to develop academic English vocabulary and comprehension
- Direct instruction that provides explicit teaching of skills or knowledge including modeling, corrective feedback, and guided practice; and
- Elements of universal design for learning (UDL) used in the general education classroom to ensure English learners can access the core curriculum (i.e., use of visuals, diagrams, role play, and breaking content into concrete steps to present new learning)
- Be written in language easily understood by general public
- Native language or other mode of communication of parent, unless clearly not feasible
- Explain types of assessment to be conducted
- State that no IEP will result from assessment without consent of parent
- Describe any recent assessments conducted (including recent Independent Education Assessments)
- Include information parents request to be considered
- Include information indicating student’s primary language and language proficiency status
- Notice must be in native language or other mode of communication, unless clearly not feasible to do so
- If native language or other mode of communication is not written, school district must:
- Translate orally or by other means
- Provide written documentation that translation has occurred
It is also a legal requirement to assess in the student’s native language when feasible. Assessing in the student’s native language provides comparative data to the IEP team about how the student performs in the native language versus English. In addition, the assessor (psychologist, speech & language specialist, special educator, etc.) can determine if similar error patterns are seen in both the native language and English (listening, speaking, reading, or writing) in order to discern if the student is having academic difficulty due to a language difference or a disability.
Assessment Report for English Learners - In addition to the basic requirements of a report, assessment reports for students classified as EL are required to have the following documentation included in the report:
- Impact of language, cultural, environmental and economic factors in learning;
- How standardized tests and techniques were altered;
- Use of the interpreters, translations for tests; include a statement of validity and reliability related to the use of such; and
- Examiner’s level of language proficiency in the language of the student and the effect on test results and overall assessment.
DEVELOPING THE IEP
It is of the utmost importance that all information pertaining to English learners be as accurate as possible to prevent any delays in state required English language proficiency assessments or ELD services. The following IEP documents are required for English learners.

CONSIDERATIONS FOR NEWCOMER STUDENTS
WELCOMING NEWCOMER STUDENTS AND FAMILIES
Newcomers may come from families that have immigrated to the United States through asylee or refugee status. Some newcomers may have experienced disruptions in their education in their native countries, and some may have adequate or advanced schooling in their home language. Most newcomers and their families will need support as they become fully integrated into their new community and adapt to U.S. schools, society, and culture. Newcomer students must not only learn how to navigate a new culture socially, but also how to function effectively in an education system and language that typically differs from their prior experience. The U.S. Department of Education highlights four basic needs:
- A welcoming environment
- High-quality academic programs designed to meet their academic and English language development needs
- Social emotional support and skills development to be successful in school and beyond
- Encouragement and support to engage in the education process
Helping Parents Understand Their Students’ Rights

Initial Placement of Newcomers
Newcomers in grades 6 through 12 must be placed in a structured English immersion program in a Newcomer ELD course, concurrent with an Emergent ELD course. They must receive integrated ELD in all core content courses and be provided with core curriculum materials in Spanish. Additional primary language support is to be provided as needed.
Supporting Newcomers' Social Emotional Needs
Those in this situation sometimes go through a “silent period” as the student and the student’s family adjusts to their new surroundings and takes in information. This silent period may last from a few days to a few months. To ensure that newcomers not only adjust but thrive academically, socially, and emotionally, school staff should offer an array of strategies and supports to develop newcomers’ skills in the classroom, in the school, and in the community at large.

While formal school programs are essential to meeting newcomers’ social emotional needs, often it is the informal caring relationships between school staff and newcomers that matter most. Such relationships enable teachers to understand and tap into students’ interests and attitudes to engage students and strengthen their learning experiences. Interactions with peers also support academic learning. While peers provide one another linguistic support when they are from the same cultural background, positive interethnic peer relations are also associated with English proficiency and academic achievement.
STUDENT PROGRESS MONITORING & RECLASSIFICATION
PROGRESS MONITORING OF EL AND RFEP STUDENTS
For English Learners, this kind of progress monitoring helps identify how well they are accessing core academic content while continuing to develop English proficiency. Regular checks of both academic and language growth ensure that instruction remains aligned with students’ language development level and academic goals. When schools use multiple measures consistently, they are better equipped to determine when an EL is ready for reclassification, when additional supports are needed, or when students are making meaningful gains that should be celebrated.
Consistent monitoring of EL and recently reclassified students helps teachers differentiate instruction, align interventions with actual areas of need, and provide timely support if, or before students fall behind. Moreover, it helps teachers ensure that reclassified students were not exited prematurely, that any academic deficits they may have incurred as a result of receiving ELD services were remedied, and that they are able to participate meaningfully in the general instructional program without language support.
Reclassification of English Learners
- they are not exited prematurely,
- any academic deficits incurred as a result of receiving ELD services have been remedied, and
- they are able to meaningfully participate in the general instructional program without ELD services.
IUSD Reclassification Criteria
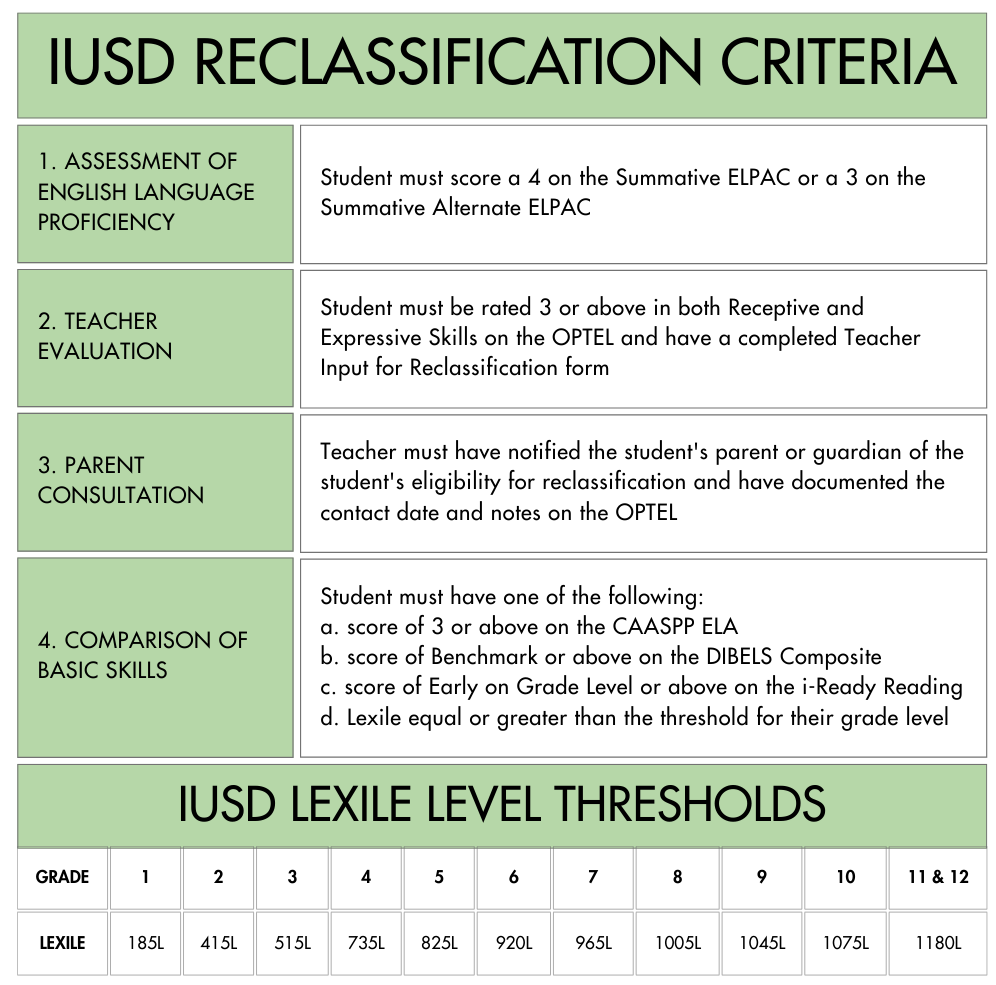
The Reclassification Process
Although the summative ELPAC is administered once each spring, Inglewood Unified makes full use of Criterion 4, which allows for local assessment data to be used as a key component of the reclassification criteria. Because local benchmarks are administered three times per year, we are able to screen students multiple times and offer reclassification opportunities throughout the year.
Before Transitioning to Middle or High School
Before Census Day
Before the Summative ELPAC
Reclassification Considerations for English Learners with Disabilities
In Inglewood Unified School District, we recognize that English Learners with disabilities often face additional barriers to reclassification when compared to their peers without disabilities. Research shows that ELs with disabilities are less likely to be reclassified, and students at the secondary level are more likely to qualify for special education services than those in the earlier grades. To promote equity and access, it is critical to implement inclusive and consistent reclassification criteria and ensure that all students are provided with appropriate support.The goal is to ensure that English Learners with disabilities have meaningful opportunities to meet the reclassification criteria through the provision of universal supports, designated accommodations, and, when appropriate, domain exemptions—not only during assessment but also consistently during classroom instruction. While all students must meet Criterion 1—a score of 4 on the Summative ELPAC or 3 on the Alternate Summative ELPAC—there is flexibility in the implementation of Criteria 2 and 4 when a student’s IEP team determines that the inability to meet standardized measures is due to the student’s disability and not a lack of English language development.
For Criterion 2, teacher evaluation must include a review of curriculum mastery and may draw from IEP goal progress and qualitative teacher observations. IEP comments, such as positive trends in speaking, writing, and classroom participation, can help demonstrate readiness for reclassification.
Criterion 4 involves comparing student performance in basic skills to that of English-proficient peers of the same age. For students with disabilities, IEP teams may determine appropriate measures that reflect equivalent performance, based on the student’s unique learning profile and in alignment with state guidance. For students taking the Alternate ELPAC, performance on the California Alternate Assessments (CAA) in ELA is used as an equivalent measure of basic skills.
While reclassification criteria must be applied consistently, the law recognizes that standardized measures may not always be appropriate for students with disabilities whose language development is impacted by their disability. In such cases, IEP teams may use alternate but equivalent measures, based on the student’s profile, IEP goals, and progress.
IUSD Alternate Reclassification Criteria for English Learners with Disabilities

Commitment to Equity

DUAL LANGUAGE PROGRAMS
In our commitment to provide a rigorous, culturally and linguistically relevant educational experience that prepares our students to become responsible and productive members of a global community, Inglewood Unified School District offers two research and standards-based dual language programs, in addition to our English Language Development program for students learning English as a second language.
The term dual language refers to any program that provides literacy and content instruction to all students through two languages and that promotes bilingualism and biliteracy, grade-level academic achievement, and sociocultural competence for all students. Dual language programs can be either one-way or two-way depending on the student population.
Upholding our vision of options and excellence, and to meet the needs of our community, Inglewood Unified offers both programs:
- Spanish Dual Language Immersion Program (two-way) at Woodworth Monroe School
- Spanish Foreign Language Program (one-way) at Frank D. Parent School
Benefits of Dual Language Education
Dual language education is a powerful, research-based approach that supports language development, academic achievement, and cultural understanding for all students. Research has shown that dual language programs are an effective way to educate English Learners, but they also offer benefits for English-only speakers. Short and long term benefits include:
- Bilingualism and Biliteracy - Students develop proficiency in two languages across speaking, listening, reading, and writing.
- Stronger Academic Outcomes - Dual language students often meet or exceed the academic performance of their peers in English-only settings, especially in upper grades.
- Enhanced Cognitive Skills - Bilingual students show increased focus, memory, problem-solving, and mental flexibility.
- Long-Term Career and College Advantages - Bilingual graduates are more competitive in global job markets and eligible for the State Seal of Biliteracy.
- Cultural Competence - Dual language education promotes empathy, cross-cultural understanding, and the ability to engage in diverse environments.
- Greater Engagement and Confidence - Students in dual language settings often feel more valued and connected to school, especially English learners.
Comparison of Dual Language Programs

Woodworth Monroe “Marineros” Dual Language Academy 
Program Model
Content and Language Allocation
Students are fully integrated for all instruction—there is no grouping by language proficiency or ability. Instead, language use is carefully planned and strategically separated by subject and time, ensuring that Spanish and English are not mixed during instruction. Concepts taught and mastered in Spanish are later reinforced in English through cross-linguistic strategies, without re-teaching the content. During instruction, teachers use only the language of instruction for all directions, explanations, and academic content, avoiding translation or code-switching. While teachers may accept student responses in either language, especially in the early grades, they consistently use strategies to encourage students to respond in the language of instruction.
The program emphasizes the development of Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP) in both Spanish and English, supporting students’ growth in literacy, content knowledge, and higher-order thinking skills. Table 13.2 shows the approximate language progression in Kindergarten through grade five. Table 13.3 outlines the language of instruction by subject area for grades six through eight, with shaded subjects indicating instruction in Spanish.

Curriculum and Instruction
SLA/SLD: Amplify Caminos
Mathematics: Savvas Envision Math
Social Studies: McGraw Hill Impact
Science: McGraw Hill Inspire Science
Student Admission and Enrollment Commitment
Once enrolled, students are expected to remain in the program through eighth grade. Enrollment will roll over each year, provided they meet district attendance and behavior expectations. Students who exceed 10 absences in a school year, or exhibit an ongoing pattern of inappropriate behavior will be referred to the DLI Leadership Committee for a review of their continued participation in the program.
All students are expected to follow district and school-wide behavior policies, including the Woodworth Monroe “Marineros” Dual Language Academy Code of Conduct. Parents are expected to address any behavioral concerns promptly and constructively. In addition to behavioral and attendance expectations, students’ academic progress will be regularly monitored. If a student is not demonstrating adequate progress, a committee review will be held to determine appropriate interventions and supports. As part of this process, the committee may also evaluate whether continued placement in the DLI program best meets the student’s academic and language development needs.
The opportunity to become bilingual and biliterate is priceless, offering lifelong academic, cognitive, and cultural benefits. However, achieving full proficiency in a second language requires dedication and sustained effort from both students and their families. Research indicates that it takes five to seven years to develop strong academic language skills in a second language. Therefore, families are expected to make a long-term commitment through eighth grade, ensuring that their student has the time and support needed to grow linguistically, academically, and socially within the program.
Frank D. Parent Foreign Language Program
Definitions

Program Model
- K-2 Grades (FLEX Model): Students engage in a flexible, theme-based introduction to Spanish. The focus is on building vocabulary through songs, stories, and hands-on activities that integrate cultural learning. The goal is to foster a love of language learning through engaging, age-appropriate activities.
- 3rd Grade and Above (FLES Model): Starting in 3rd grade, the curriculum follows a more structured FLES model, emphasizing the development of language skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Students begin to use more conversational Spanish and apply language skills to content areas, promoting interdisciplinary learning.
- Upper Grades (6-8): Although only currently available in grades K-5, the program will be expanded to middle school grades, offering more advanced language study in preparation for high school Spanish or dual language immersion programs. This ensures that students maintain and expand their language skills throughout their time at the school.
Curriculum and Instruction
The Spanish foreign language program aligns with the California World Languages Standards and follows a phased implementation model. Students in grades K-2 use the FLEX (Foreign Language Experience) model, focusing on vocabulary acquisition through songs, stories, and cultural activities. In grades 3 and above, the FLES (Foreign Language in Elementary Schools) model emphasizes conversational Spanish and interdisciplinary learning.
To maintain high-quality instruction and alignment with program goals, all Spanish foreign language educators and instructional staff are expected to attend and engage in ongoing training focused on curriculum, instruction, foreign language education, and multicultural competencies; and participate in program-wide collaboration and reflection to maintain instructional consistency and uphold program integrity.
State Seal of Biliteracy Pathway
The Inglewood Unified School District recognizes the value of this Seal, and the importance it places on bilingualism and biliteracy. In order to encourage students to continue on the Pathway to Biliteracy, the WM Marineros Dual Language Academy and the Frank D. Parent Foreign Language Program celebrate student growth and accomplishments at the end of the following grades, based on specific English and Spanish proficiency criteria:
Kindergarten - Academy Certificate of Initial Steps Toward Biliteracy: Listening and Speaking
Third grade - Academy Certificate of Initial steps toward biliteracy: Reading and writing
Fifth grade - Academy Certificate of Linguistic and Academic Proficiency
Eighth grade - IUSD Certificate of Linguistic and Academic Proficiency
Family Commitment and Engagement
Parents are also expected to become active partners in their student’s education at both the school and district level. This may include participating in parent-teacher conferences, attending school events, serving on advisory committees, or joining family workshops related to multilingual education. Research consistently shows that students whose parents are involved in their education demonstrate higher academic achievement, better attendance, improved behavior, and a stronger interest in learning. In the dual language setting, this partnership is especially powerful, as it reinforces the value of bilingualism and strengthens the connection between home and school.
PRESCHOOL DUAL LANGUAGE LEARNERS
DETERMINATION OF PRESCHOOL DUAL LANGUAGE LEARNER STATUS
California state preschool programs must determine Dual Language Learner status for every student enrolled by one of two approaches:
- Completing the Family Language Instrument and participating in the Family Language Interest Interview, within 30 calendar days of:
- the first day the student is scheduled to receive CSPP services, for part-day enrollment.
- the date that the program certifies the family for CSPP services, for full-day enrollment.
- Through Teacher Designation, only after 30 calendar days, and a parent chooses not to answer questions in the Family Language Instrument, the student has been identified as “not a DLL,” and after meeting with the parent or guardian.
The Family Language Instrument
A student’s experience with one or more languages is an asset to build on in the early childhood setting. It is critical to consider the student’s communication in all the languages that he or she is learning in order to have an accurate picture of the student’s knowledge and skills.
Parents seeking enrollment in the Inglewood Unified School District State Preschool Program through the Child Development Center (CDC) are provided the Family Language Instrument (FLI) to identify and understand each student’s language background. The instrument consists of the following four questions:
- Which language(s) does your student hear at home?
- Which language(s) does your student hear in their neighborhood and community?
- Which language(s) does your student understand?
- Which language(s) does your student speak?
Non-Dual Language Learner (non-DLL) is designated if English is the answer to FLI questions 1, 3 and 4. The language students hear in their neighborhood and community (question 2) does not determine language proficiency.
Dual Language Learner (DLL) is designated if at least one response is a language other than English on FLI questions 1, 3, or 4. If the student is identified as a Dual Language Learner, parents will be asked to complete a Family Language and Interest Interview.
The Family Language and Interest Interview
The interview takes at least 30 minutes and may be conducted by phone or online; although best practice is to conduct it in person. To the extent possible, the interview will be conducted in the language the family speaks.
The purpose of this interview is to support relationship building with families of students who are identified as Dual Language Learners and to learn more about each student’s experiences with language. When adults understand students’ past experiences with language(s), they are able to build upon those experiences and better support students’ development.
The interview is designed to make families feel comfortable in answering questions about their student and for the program to encourage families to continue developing their student’s home language in the home. The interview includes sharing resources about the benefits of multilingualism with families. The interview also supports Inglewood Unified in:
- Building a relationship and trust with the student’s family member(s)
- Learning about students’ past experiences with language(s) in order to best support their optimal progress and development in our program
- Helping families understand the benefits of multilingualism and the important role of the home language in supporting English development
- Encouraging families to continue developing their student’s home language in the home
- Having a better understanding of the different languages and cultures in the classroom to make program-wide decisions on resources (e.g., purchasing books in the different languages represented by students and families)
The information we gather is used to inform and plan program curriculum, develop learning strategies, create professional development opportunities, and to strengthen family partnerships to improve support for PDLL students. It is important to remember that a DLL identification will serve them only in preschool, and is different from any identification process or program a student might later receive if classified as an English Learner in Kindergarten through 12th grade.
Teacher Designation
If within 30 calendar days from the date of enrollment through observations, the student demonstrates he or she speaks, responds to, or understands a language other than English, the student’s teacher must meet and share these documented student observations with the family and review the DLL identification process and the FLI to ensure proper designation. During this meeting, the CDE recommends that the following be shared with the family:
- The benefits of multilingualism and home language development
- How proper designation can support the program in supporting the student with English and home language development
- Clarification that this designation is specific to CSPP and will not apply in elementary school and beyond
- Address any other hesitations or concerns the family might have around the process
If after meeting with the family to ensure proper designation, the parent or guardian still chooses not to update their answers or complete the FLI, the student’s teacher may designate the student as a DLL through a Teacher Designation.
Teacher Designation can only occur after 30 calendar days and after meeting with the parent or guardian. Written observations and documentation from conversations with the family about their responses to the FLI must be included in the family file. Teachers should attempt to obtain and document responses to questions 4, 6, 7, and 8 from the family interview within 30 calendar days of designation as these responses are still required to be reported.
Foundations in English Language Development
The English Language Development (ELD) domain is specifically designed for students whose home language is not English. It focuses on promoting early English language acquisition while respecting and valuing the student’s home language and cultural background. The knowledge and skill areas in this domain are aligned with the California English Language Development standards Kindergarten through 12th grade, are organized into three stages of language development—Beginning, Middle, and Later—and span the key strands of Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing.

English Language Development Level Progression

English Language Development Strands

PARENT & FAMILY ENGAGEMENT
PARENT & FAMILY ENGAGEMENT
English Learner Advisory Committees
- Development of a district master plan for education programs and services for English learners. The district master plan will take into consideration the school site master plans.
- Conducting a district wide needs assessment on a school-by-school basis.
- Establishment of district program, goals, and objectives for programs and services for English learners.
- Development of a plan to ensure compliance with any applicable teacher and/or teacher aide requirements.
- Review and comment on the school district reclassification procedures.
- Review and comment on the written notifications required to be sent to parents and guardians.
- LCAP goals, objectives and actions
- Achievement data (CAASPP, ELPAC, i-Ready)
- Suspension and chronic absenteeism data
- Federal, state and local funding for English learner programs and services


ELAC is a school-level committee composed of parents, staff, and community members designated to advise school administrators on English language programs and services. Every school with 21 or more English learners must have an ELAC and meet at least five times per year to accomplish the following tasks as required by the state of California:
- Advising the principal and staff in the development of a site plan for English learners and submitting the plan to the School Site Council for consideration of inclusion in the School Plan for Student Achievement.
- Assisting in the development of the school-wide needs assessment.
- Making parents aware of the importance of regular school attendance.
- Electing at least one member to the District English Learner Advisory Committee.
- SPSA goals, actions and strategies for English learners
- Achievement data (CAASPP, ELPAC, i-Ready)
- Suspension and chronic absenteeism data
- Federal, state and local funding for English learner programs and services

EL Services Instructional Coach









